How to Recycle Textile Waste: A Sustainable Approach to Minimize Environmental Impact
Introduction:
Textile waste is a pressing global issue that demands immediate attention. As the fashion industry continues to thrive, the accumulation of discarded textiles poses a significant threat to the environment. However, with a growing awareness of sustainable practices, recycling textile waste has emerged as a viable solution. In this blog post, we will explore various methods and techniques that can be employed to effectively recycle textile waste. By adopting these strategies, we can contribute to the conservation of resources, reduction of pollution, and the creation of a more sustainable future.
I. Understanding Textile Waste:
1.1 The Scale of the Problem:
The fashion industry generates a colossal amount of textile waste annually, with a substantial portion ending up in landfills or incinerators. This waste includes both pre-consumer waste (generated during the manufacturing process) and post-consumer waste (discarded by consumers).
1.2 Types of Textile Waste:
Textile waste encompasses a wide range of materials, including clothing, accessories, household fabrics, and industrial textiles. These textiles can be made from natural fibers (such as cotton, silk, or wool) or synthetic fibers (such as polyester or nylon).
II. Recycling Techniques for Textile Waste:
2.1 Mechanical Recycling:
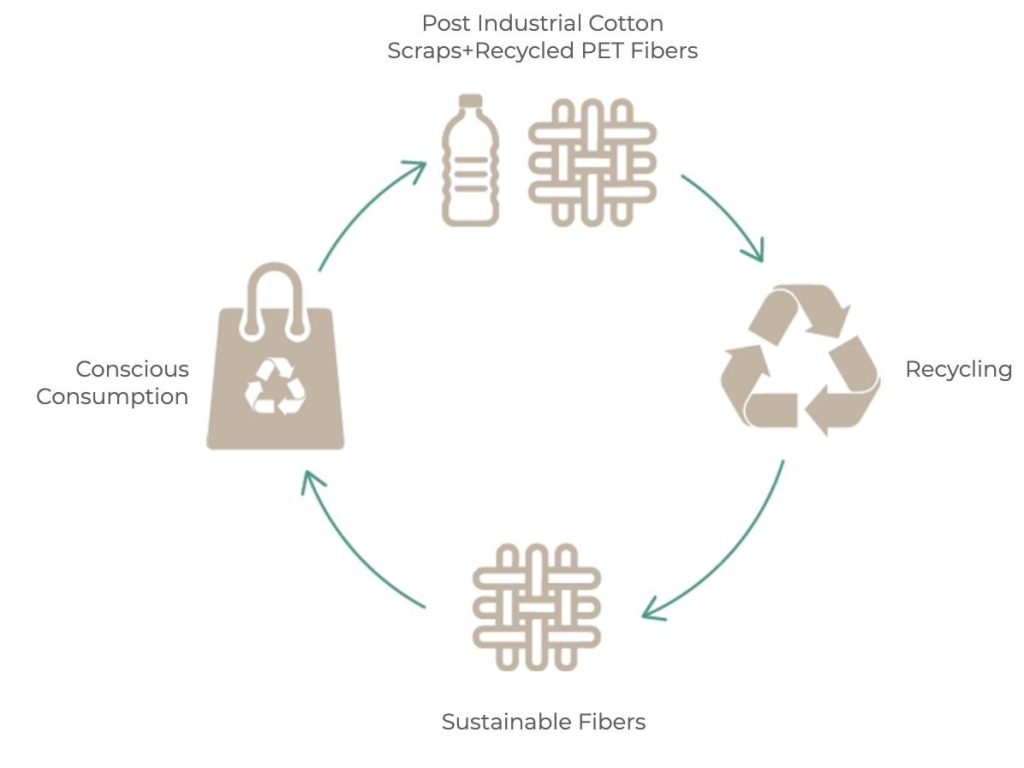
Mechanical recycling involves the breakdown of textile waste into fibers that can be reused in the production of new textiles. This process typically consists of sorting, shredding, and carding to convert waste into recycled fibers.
2.2 Chemical Recycling:
Chemical recycling techniques employ various chemical processes to dissolve, depolymerize, or melt textile waste into its original constituents. This enables the production of new fibers or other products.
2.3 Upcycling:
Upcycling involves transforming textile waste into higher-value products without breaking down the original fibers. This approach focuses on creativity and innovation, repurposing textiles into new clothing, accessories, or home furnishings.
2.4 Energy Recovery:
In cases where recycling is not feasible due to the condition or composition of the textile waste, energy recovery can be employed. Through incineration with energy capture, the waste is used as a source of energy, minimizing its environmental impact.
III. Implementing Textile Waste Recycling
3.1 Collection and Sorting:
The first step in textile waste recycling is efficient collection and sorting. This can be achieved through the establishment of collection centers, partnerships with textile manufacturers, and collaborations with local communities.
3.2 Consumer Education:
Educating consumers about the importance of recycling textile waste is crucial. Informative campaigns and awareness programs can help individuals make informed choices regarding responsible disposal and encourage them to support recycling initiatives.
3.3 Industry Collaboration:
The fashion industry plays a pivotal role in reducing textile waste. Collaborative efforts among designers, manufacturers, and retailers can promote responsible production, encourage sustainable design practices, and facilitate the integration of recycled textiles into new products.
3.4 Supporting Innovations:
Encouraging research and development of innovative recycling technologies is essential for the advancement of textile waste recycling. Investment in new techniques, such as biodegradable fibers or digital recycling methods, can revolutionize the industry’s sustainability efforts.
IV. Challenges and Future Outlook
4.1 Infrastructure and Technology:
Developing effective infrastructure and adopting advanced technologies are vital for scaling up textile waste recycling processes. Investment in modern machinery, recycling facilities, and collection networks can overcome logistical challenges and streamline operations.
4.2 Consumer Mindset and Behavior:
Shifting consumer attitudes and behaviors toward sustainable fashion choices is critical. Emphasizing the environmental impact of textile waste and the value of recycled products can drive demand and encourage responsible consumption.
4.3 Policy and Regulations:
Governments and regulatory bodies need to establish policies and regulations that incentivize and enforce textile waste recycling. Providing financial incentives, implementing extended producer responsibility programs, and setting clear recycling targets can facilitate industry-wide compliance.
4.4 Collaborative Initiatives:
Encouraging partnerships and collaborations between governments, businesses, and non-profit organizations is key to fostering a circular economy for textiles. Joint efforts can drive research, share best practices, and create a supportive ecosystem for sustainable fashion.
Conclusion:
Recycling textile waste is an essential step toward mitigating the environmental impact of the fashion industry. By adopting various recycling techniques, implementing effective strategies, and fostering collaboration, we can significantly reduce the accumulation of textile waste and promote a sustainable future. It is our collective responsibility to embrace these solutions and drive the transformation toward a circular economy. Together, let us embark on this journey to conserve resources, minimize pollution, and create a more sustainable and responsible fashion industry.